Development of the Hemispherical Rotational Modulation Collimator Imaging System
- Journal
- IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science
- Vol. (No.), pp.
- 66 (9), 2114-2122 (Sep 2019)
- Year
- 2020-2014
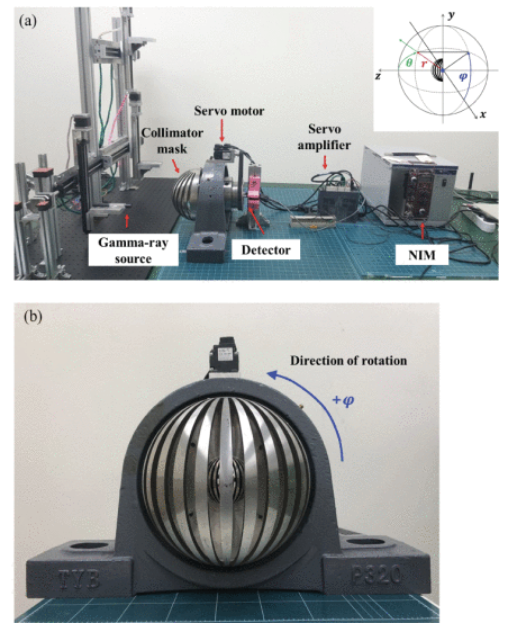
A rotational modulation collimator (RMC) imager consists of two collimator masks rotating ahead of a non-position-sensitive detector. It requires fewer detectors than other radiation imagers, which offers the possibility of reducing the instrument complexity and cost. A hemispherical RMC (H-RMC) is capable of imaging radiation with a significantly better field of view (FOV) than conventional RMCs with cylindrical geometry. In this study, a novel hemispherical collimator design was developed in order to extend the FOV to nearly 2π. We designed the hemispherical mask considering several parameters, demonstrated the measured performance of the instrument, and showed the two-dimensional (2-D) reconstructed images of radiation distribution. The H-RMC imager described herein featured a symmetric design that leads to degenerate reconstruction of two possible source locations for a single true source location. Nevertheless, it has been possible to establish that the maximum likelihood expectation maximization (MLEM) approach with regularization technique significantly reduced the artifact of misestimated source positions and improved the values of signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and the structural similarity (SSIM) index compared to the conventional MLEM method.